The government has no national plan for the defence of the UK or the mobilisation of its people and industry in a war despite renewed threats of conflict, Sky News has learnt.
With ministers warning that Britain is moving to a “pre-war world” amid mounting concerns about Russia, China and Iran, it can be revealed that officials have started to develop a cross-government “national defence plan”.
But any shift back to a Cold War-style, ready-for-war-footing would require political leaders to make defence a genuinely national effort once again – rather than something that is just delivered by the armed forces, according to interviews with multiple defence sources, former senior officers and academics.
They said such a move would need a lot more investment in defence and much better communication with the public about the need for everyone to play their part in strengthening UK resilience and deterring aggression.
“We have to have a national defence plan,” a senior defence source said, speaking on condition of anonymity.
“It should involve what government arrangements would look like in the period before armed conflict and the transition to war.”
It can also be revealed:
• A two-day “war game” is set to take place next week, involving officials from the Ministry of Defence, Cabinet Office, Home Office and other departments, to talk through how the country would respond to an armed attack
• A paper is circulating in Whitehall that examines what can be learnt from an old but comprehensive system of plans called the Government War Book – now sitting in the National Archives – that once detailed how the UK would transition from peace to war
• Sources say lessons could also be drawn from how the UK mobilised its industrial base ahead of the Second World War when it created a network of “shadow factories” that vastly expanded production capacity for aircraft such as Spitfires
Grant Shapps, the defence secretary, used a speech in January to raise the spectre of a “pre-war world”.
He also forecast that in five years’ time “we could be looking at multiple theatres involving Russia, China, Iran and North Korea”.
Given the warning signs, Sky News has decided to explore how prepared the UK government, its military and the entire nation are for the possibility of armed conflict.
We have also looked back at the last time Britain was in a pre-war world, in the five years before the Second World War that erupted in 1939, as well as how this country subsequently dealt with the possibility of World War 3, including nuclear attack, during the Cold War years.
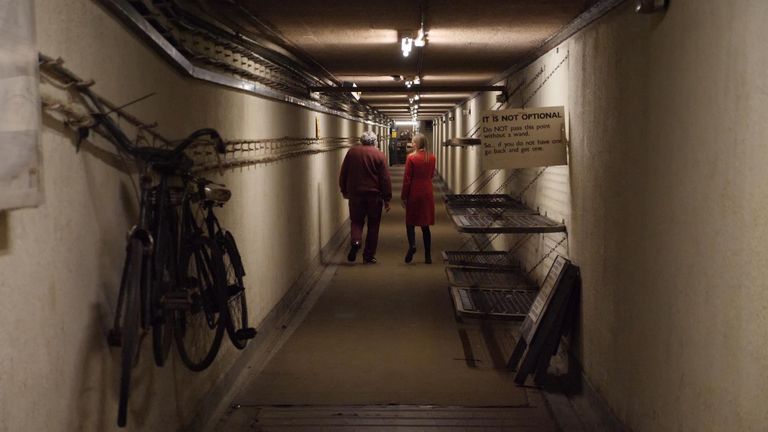
In the first instalment of a series – called Prepared For War? – we visited the National Archives to view a Government War Book; travelled to an old nuclear bunker once part of a secret plan to support the nation in the event of nuclear war; and examined the legacy the World War 2 shadow factories, which built the weapons that helped defeat the Nazis.
‘The problem is, there is no plan’
Setting out the challenge, Keith Dear, a former regular Royal Air Force intelligence officer who worked as an adviser to the prime minister between 2020 and 2021, when Boris Johnson was in power, said he had been unable to find any kind of detailed plan for war while in government.
He said specific planning is required to explain “what we think could happen, and specifically who needs to do what, when, to respond effectively”.
In an exclusive article for Sky News, he wrote: “Such plans are essential not only to avoid scrambling disorder and early defeats, but also so that our adversaries, awed by our preparedness, are deterred from fighting in the first place.
“The problem is, there is no plan.”
Instead, defence sources said the UK today relies on its arsenal of nuclear weapons and membership of the NATO military alliance to deter threats.
“The government assumes deterrence will always work, but no one stops to ask: what if it doesn’t?” the senior defence source claimed.
The apparent lack of a national defence plan means the army, Royal Navy and Royal Air Force – let alone the readiness of the civilian population and industrial base – are not designed to fight an enduring war of survival, the defence sources said.
“Our air defence [the ability to fend off incoming enemy missiles and drones] is dangerously thin and coastal defence is all-but non-existent,” the senior defence source said.
There is also a shortage of weapons and ammunition, while the size of all three services, both regular and reserve, is a fraction of the force that was kept at a high level of readiness during the Cold War in case of World War Three.
General Sir Richard Barrons, a former top commander, said he raised the idea inside government just over a decade ago about the need to rebuild national defence and resilience because of a growing threat from Moscow.
But “the implications of thinking about the revitalisation of a risk from Russia were unpalatable and expensive and denial – frankly – was cheaper”, he said.
War books
In the wake of Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine two years ago, NATO refreshed its war plans for defending the whole of the now 32-nation alliance.
But the UK used to have its own corresponding set of national plans – set out in the Government War Book – that would trigger certain internal measures if the alliance decided to transition from peace to war.
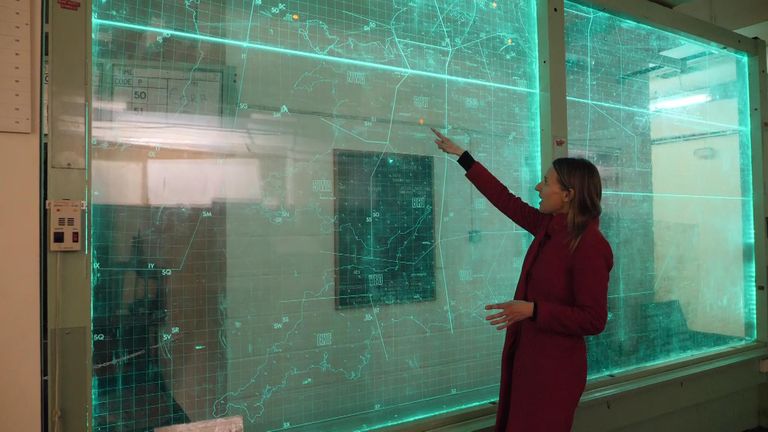
A 1976 copy of the war book – a large bundle of hand-typed pages, bound together by string – offered a sense of how seriously the UK once took national defence planning.
Stored at the National Archives in Kew, west London, the war book contained detailed lists and signposted the way to complementary plans about how to mobilise not just the military but also civilians and industry in a crisis as well as shutting schools, clearing hospitals, rationing food and even storing national treasures.
Conceived around the end of the First World War, the government’s collection of top secret, regularly rehearsed and updated war books ensured by the height of the Cold War the UK was one of the best prepared nations in the world – and most resilient.
That all changed after the collapse of the Soviet Union as Western governments no longer felt the existential threat of global war.
By the early 2000s, the entire UK war book system, which cost a lot to maintain, was quietly shelved as the then government’s focus switched to the threat from Islamist terrorism and fighting foreign wars in Afghanistan and Iraq.
It means most senior officials in today’s Whitehall will barely have any professional memory of how the state functioned during the Cold War years, let alone the two world wars.
Jonathan Boff, a professor of military history at Birmingham University, said the UK should think about producing a modern-day version of the war books.
“Some of that kind of thinking – the thinking that takes you from: we don’t need to worry about any of that to: actually if we did want to worry about that, how might we do it? – I think that’s really important,” he said.
Risk register and intelligence framework
Asked about the allegation that the UK has no national plan for the outbreak of war, a spokesperson for the Cabinet Office said the country has “robust plans in place for a range of potential emergencies and scenarios with plans and supporting arrangements developed, refined and tested over many years”.
This includes the Civil Contingencies Act, a government resilience framework, a National Risk Register and a strengthening of ties with a network of local resilience forums across the country that are tasked with responding to emergencies. There is also a new directorate in the Cabinet Office tasked with further enhancing resilience.
“As part of broad emergency response capabilities, all local resilience forums have plans in place to respond to a range of scenarios,” the spokesperson said.
“The government continues to review the risk landscape, including threats to the UK from overseas.”
Yet a flick through the National Risk Register offers a lot more information on floods, pandemics, terrorism and cyber attacks than what to do in the event of war.
A number of local resilience forums approached by Sky News also confirmed that they do not have specific war plans or planning for a nuclear strike – something that would have been a top priority for local governments during the Cold War.
Shadow factories
The funding priorities for many NATO allies, including the UK, changed following the demise of the Soviet Union in 1991, with investment switching away from defence to areas such as health and social services – more popular in peacetime.
This has started to be reversed following Vladimir Putin’s invasion of Ukraine, but defence sources said it must happen with much greater urgency – especially as Russia is on a war footing and has even threatened the use of nuclear weapons.
Back in 1935, when war with Adolf Hitler’s Germany was looming, the UK began rapidly growing its manufacturing base to build more aircraft, converting automotive plants to produce Spitfires, Hurricanes, Lancaster bombers and other kit.
A programme, called the “shadow scheme”, under the then Air Ministry, saw the construction of “shadow factories” next to existing automotive-turned-aircraft plants.
But the UK’s manufacturing landscape has consolidated in recent years, while many weapons are imported, making it harder to revive sovereign industrial capacity at speed.
Keith Dear, the former Downing Street adviser, pointed at the difficulties Britain has had increasing the production of artillery shells and other ammunition to support Ukraine.
“Our inability to supply anything like enough munitions or weapons to Ukraine, shows also how hollowed out we have become by buying and building armed forces to no coherent war-fighting plan,” he wrote. “Weapons without ammunition are useless.”
‘We aren’t ready – but don’t tell Putin’
Southampton is a reminder of the UK’s former wartime resilience.
The home of the Spitfire, production lines were dispersed around the city after German bombers attacked its two main aircraft factories early on in the Second World War.
Today, Alan Matlock, a local man, heads a group called the Spitfire Makers Charitable Trust that raises awareness about the historic bravery of Southampton’s residents.
“The frontline did run through these factories,” he said. “And there were a large number [of people] who paid the ultimate price.”
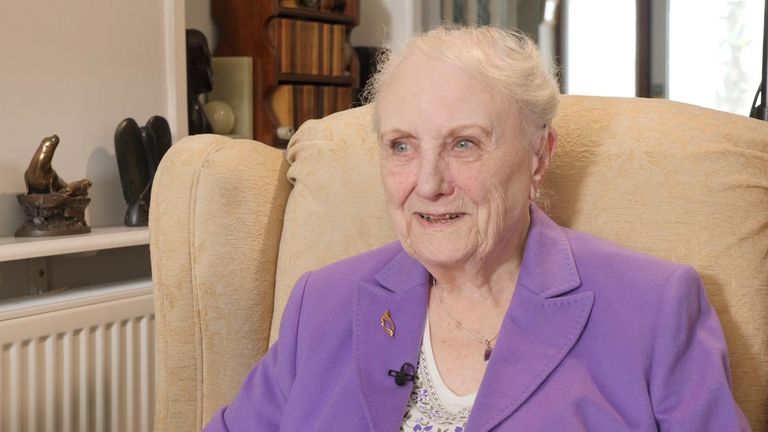
Vera Saxby, who turns 100 in August, decided to do secretarial work for a company that made parts for Spitfires during the war after a German bomb exploded in her garden.
“We really thought we were doing something good,” she said.
However, resting in an armchair in her house in a Southampton suburb, Mrs Saxby said she did not think Britain was very resilient anymore – pointing in particular to the reduction in heavy industry, such as steel works and car plants that were so vital during the last war.
Asked if it was worrying, Mrs Saxby said: “Well it is but I’m too old to worry anymore… I can’t see how we would defend ourselves – but don’t tell Putin that.”
A spokesperson for the Ministry of Defence said: “We have a range of plans in place to secure and defend the country, which are reviewed and adapted in response to international security developments… These plans will be integrated as part of our contribution to ongoing work to develop a cross-government National Defence Plan, which will further enhance our preparedness and strengthen our deterrence for the future.”